Visa Status
The H-1B & J-1 visas
Understanding
Travel Visas
The H-1B and J-1 visas are both non-immigrant work-related visas in the U.S., but they serve different purposes and have different requirements. Here’s a comparison:

H-1B VISA
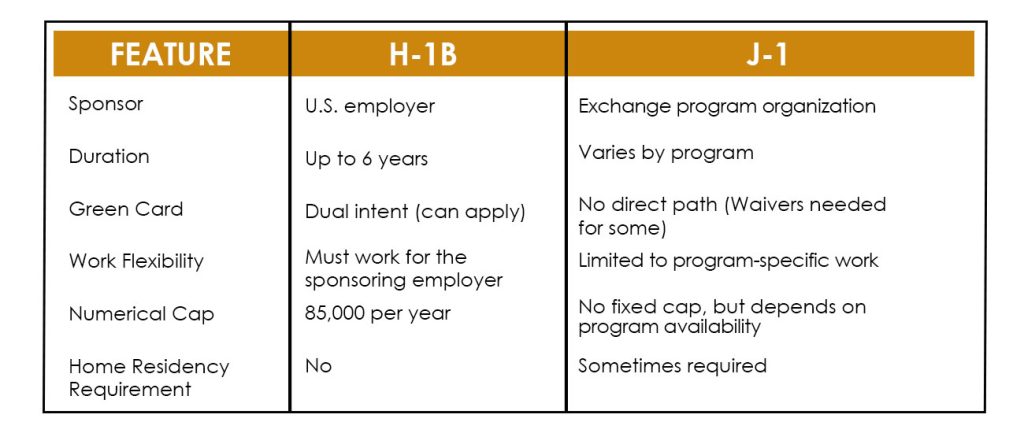
- Eligibility: Requires at least a bachelor’s degree (or equivalent experience).
- Purpose: For skilled foreign workers in specialty occupations (e.g., IT, engineering, healthcare, finance).
- Sponsorship: Requires a U.S. employer to sponsor the applicant.
- Duration: Initially granted for up to 3 years, extendable to a maximum of 6 years.
- Work Restrictions: Can only work for the sponsoring employer.
- Path to Green Card: Dual intent—can apply for a Green Card while on H-1B.
- Numerical Cap: Limited to 85,000 new visas per year (65,000 for general applicants and 20,000 for those with U.S. master’s degrees).
- Key Industries: Tech, finance, engineering, healthcare, and academia.

J-1 VISA
- Purpose: For exchange visitors in educational, cultural, or research programs (e.g., professors, researchers, interns, trainees, au pairs).
- Sponsorship: Requires a designated exchange program sponsor (e.g., universities, research institutions, or cultural exchange organizations).
- Eligibility: Varies by program; may require a degree, experience, or affiliation with a university or organization.
- Duration: Depends on the specific J-1 category (ranges from a few months to several years).
Key differences